Nevada Geography: The Land
Geography and Landforms of Nevada
 Find
an overview of Nevada geography, topography, geographic land regions, land areas, and major rivers.
Find
an overview of Nevada geography, topography, geographic land regions, land areas, and major rivers.
Access Nevada almanac furnishing more details on the state geography, geographical and land regions, climate and weather, elevation, land areas, bordering states, and other statistical data.
Most of the state of Nevada lies within the Great Basin, a large desert area that extends into Utah, California, Oregon, Wyoming, and Idaho. The land is broken up by more than 30 mountain ranges that extend from north to south throughout the state.
Elevation in the Basin region varies from a few
hundred feet above sea level near the Colorado River to 13,000 feet in the southwest. Nevada's highest point, Boundary Peak (13,140 feet) is located
here.
Nevada is one of the driest states in the nation. Much of its landscape consists of arid stretches of land covered with sagebrush and creosote bush.
Most of the state's rivers run only during the wet season (December through June) and go nowhere. They empty into lakes with no outlets or flow into
wide, shallow alkali sinks. When the water evaporates in the summer, the sinks become mud flats or dry lakes.
Hot springs and geysers are remnants of the dying volcanoes that once populated Nevada.
Nevada Highest, Lowest, & Mean Elevations |
|
|---|---|
| Mean Elevation | 5,500 ft. |
| Highest Point | Boundary Peak 13,140 ft. |
| Lowest Point | Colorado River 479 ft. |
Nevada Land Area (Square Miles) |
|
| Geographic Center | In Lander County, 26 mi. SE of Austin Longitude: 116° 55.9'W Latitude: 39° 30.3'N |
| Total Area | 110,560.71 sq. mi. 7th |
| Land Area | 109,825.99 sq. mi. 99.34% |
| Water Area | 734.71 sq. mi. 0.66% |
| Forested Land Area | 14.1% |
| Dimensions (Length - Width) |
490 miles - 320 miles |
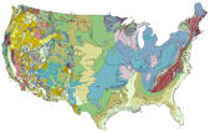
Nevada: Physiographic Regions
The state can be divided into three land regions:
- the Columbia Plateau,
- the Sierra Nevada, and
- the Basin and Range Region.
Columbia Plateau
In the northeastern corner of Nevada, the land is supported by lava bedrock. Rivers and streams have cut deeply into the bedrock, leaving deep canyons with steep ridges. Near the Idaho border the land turns to open prairie.
This is an arid sagebrush steppe and grassland surrounded on the north, west, and east by moister, predominantly forested, mountainous ecological regions. It is an oddly shaped physiographic area that covers portions of Washington, Oregon, Idaho, Nevada, and a small piece of northeast California. It consists of arid tablelands, intermontane basins, dissected lava plains, and widely scattered low mountains. There is a more subtle transition to the Basin and Range to the south in which hotter lowlands are dissected by isolated mountain ranges.
Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada is the rugged mountain range that cuts across a portion of Nevada south of Carson City. Lake Tahoe, a beautiful glacial lake, on the California/Nevada border lies in one of the valleys of the Sierra Nevada.
The Sierra Nevada range, mostly within California and barely extending into Nevada, rises sharply from the arid basin and range on the east and slopes gently toward the Central Valley of California on the west. Vegetation at lower elevations is dominated by lodgepole pine on the east and ponderosa pine on the west, with fir, spruce, and alpine tundra at higher elevations.
Basin and Range
The Basin and Range Region is bordered on the west by the Sierra Nevada. This region is divided by more than 150 mountain ranges running from north to south. In the center of the state are the Toiyabe and Toquima mountain ranges. In the east are the Snake and Toana mountain ranges. Scattered between all of the ranges are buttes (single lone hills) and mesas (flat-topped mountains) as well as flat valleys with lakes or alkalie flats.
The Basin and Range is a large physiographic area covering most of Nevada, part of eastern California, western Utah, and southeast Idaho. It lies in the rainshadow of the Sierra Nevada, south of the Columbia Plateau and north of the Mohave Desert, and is a mosaic of xeric basins, scattered mountains, and salt flats. It is hotter and contains more and higher mountains than the Columbia Plateau, with more perennial streams and ponderosa pine forest at the higher elevations. Compared to the Mojave Desert, it is not as hot and is more dominated by shrubland and less by grassland.
Nevada Landscape and Landforms:
Mojave Desert
In the "Great American Desert" of the Southwest, the Mohave lies between and is intermediate in nature between the Great Basin to the north and the Sonoran Desert to the south and east. It is mostly in southeast California but extends also into southern Nevada, northwest Arizona, a very small part of southwest Utah, and lies in the rainshadow of the Southern California Ranges to the west. Its most prominent features are broad, sparsely vegetated plains. However, it also includes dry lakes, sharply rising buttes and relatively small mountain ranges, and its eastern portion is cut through by the Colorado River. It is generally a higher elevation desert than the Sonoran, although elevation descends to -300 m in Death Valley. Low precipitation, most falling in winter, with low winter and high summer temperatures are characteristic.